Table Of Content
Hence, each study will require thorough review of the protocol by the institutional review board before approval and implementation. In simple randomization, the subjects are randomly allocated to experiment/intervention groups based on a constant probability. That is, if there are two groups A and B, the subject has a 0.5 probability of being allocated to either group. This can be performed in multiple ways, and one of which being as simple as a ‘flip of a coin’ to using random tables or numbers.17 The advantage of using this methodology is that it eliminates selection bias. However, the disadvantage with this methodology is that an imbalance in the number allocated to each group as well as the prognostic factors between groups. Every now and then during clinical practice, we come across a case that is atypical or ‘out of the norm’ type of clinical presentation.
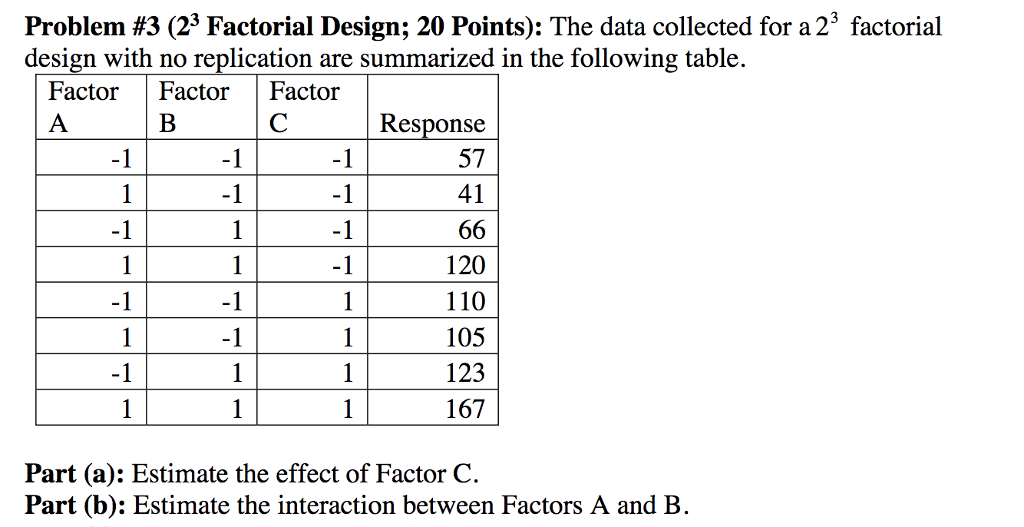
3.5. Identifying main effects and interactions¶
A common one to select is "Residuals versus fits" which shows how the variance between the predicted values from the model and the actual values. The default factors are named "A", "B", "C", and "D" and have respective high and low levels of 1 and -1. The name of the factors can be changed by simply clicking in the box and typing a new name. Additionally, the low and high levels for each factor can be modified in this menu.
1. Multiple Dependent Variables¶

Additionally, a low and high value are initially listed as -1 and 1, where -1 is the low and 1 is the high value. The low and high levels for each factor can be changed to their actual values in this menu. Minitab 15 Statistical Software is a powerful statistics program capable of performing regressions, ANOVA, control charts, DOE, and much more. Minitab is especially useful for creating and analyzing the results for DOE studies. It is possible to create factorial, response surface, mixture, and taguchi method DOEs in Minitab.
Types of Factorial Designs
However, these differences will need to be accounted during analysis of results. For example, imagine that researchers want to test the effects of a memory-enhancing drug. Participants are given one of three different drug doses, and then asked to either complete a simple or complex memory task. When the difference in response between the levels of one factor is not the same at all the levels of the other factor, there is an interaction between the factors. This can be seen by noting that the pattern of entries in each A column is the same as the pattern of the first component of "cell". (If necessary, sorting the table on A will show this.) Thus these two vectors belong to the main effect of A.
With widespread adoption of factorial design, social scientists could now... When designing a factorial trial, the main intention of researchers is to achieve ‘two trials for the price of one’. To do so, an important assumption is that the effects of the different active interventions are independent. In other words, there should be no interaction (no synergy or antagonism) between the treatments.
Screening autism-associated environmental factors in differentiating human neural progenitors with fractional factorial ... - Nature.com
Screening autism-associated environmental factors in differentiating human neural progenitors with fractional factorial ....
Posted: Thu, 29 Jun 2023 07:00:00 GMT [source]
Factors, Main Effects, and Interactions
(In reality, there was no other participant.) Then they gave each participant 10 points (which could later be converted to money) to split with the “partner” in whatever way he or she decided. Because the participants were the “dictators,” they could even keep all 10 points for themselves if they wanted to. Factor analysis does not tell us that people are either extraverted or conscientious or that they like either “reflective and complex” music or “intense and rebellious” music. So people who are high in extraversion might be high or low in conscientiousness, and people who like reflective and complex music might or might not also like intense and rebellious music. The second point is that factor analysis reveals only the underlying structure of the variables. It is up to researchers to interpret and label the factors and to explain the origin of that particular factor structure.
After all the trials were performed, the wt% methanol remaining in the biodiesel and number of theoretical stages achieved were calculated. The figure below contains the DOE table of trials including the two responses. It is clear that in order to find the total factorial effects, you would have to find the main effects of the variable and then the coefficients. Other than these slight detractions, a factorial design is a mainstay of many scientific disciplines, delivering great results in the field.
Both of these graphs only contain one main effect, since only dose has an effect the percentage of seizures. Whereas, graphs three and four have two main effects, since dose and age both have an effect on the percentage of seizures. Social researchers often use factorial designs to assess the effects of educational methods, whilst taking into account the influence of socio-economic factors and background. An advantage of these graphs is that they display means in all four conditions of the design. Someone looking at this graph alone would have to guesstimate the main effects. If we made a separate graph for the main effect of shoes we should see a difference of 1 inch between conditions.
2.5. Graphing the Results of Factorial Experiments¶
In this experiment, they manipulated participants’ feelings of disgust by testing them in either a clean room or a messy room that contained dirty dishes, an overflowing wastebasket, and a chewed-up pen. They also used a self-report questionnaire to measure the amount of attention that people pay to their own bodily sensations. They measured their primary dependent variable, the harshness of people’s moral judgments, by describing different behaviors (e.g., eating one’s dead dog, failing to return a found wallet) and having participants rate the moral acceptability of each one on a scale of 1 to 7.
First, it is highly unlikely that such testing would have distinguished amongst the three leading combinations shown in Figure 1 (the differences in outcomes are too small). Second, such tests would have been grievously underpowered, and increasing the sample size to supply the needed power would have compromised the efficiency of the factorial design (Green et al., 2002). This, of course, has limitations, such as not permitting strong inference regarding the source(s) of the interaction.
Dr. Loh conducts research and consults for the pharmaceutical industry on statistical methodology, but the activities are unrelated to smoking or tobacco dependence treatment. Researchers want to determine how the amount of sleep a person gets the night before an exam impacts performance on a math test the next day. But the experimenters also know that many people like to have a cup of coffee (or two) in the morning to help them get going.
For example, both the red and green bars for IV1 level 1 are higher than IV1 Level 2. And, both of the red bars (IV2 level 1) are higher than the green bars (IV2 level 2). After you become comfortable with interpreting data in these different formats, you should be able to quickly identify the pattern of main effects and interactions. For example, you would be able to notice that all of these graphs and tables show evidence for two main effects and one interaction. The red bars show the conditions where people wear hats, and the green bars show the conditions where people do not wear hats. For both levels of the wearing shoes variable, the red bars are higher than the green bars.
If no adherence main effect is found, is that because this component was inconsistently delivered (adjusted for each medication)? In sum, investigators should be cognizant of the possible effects of such intervention adjustment and consider options for addressing them (e.g., by making only essential adjustments to a component, nesting an adjusted factor in the design). Thus, investigators must decide if they wish to directly compare two treatment conditions (and these may be multicomponential) with one another, without the results being affected by the presence of other experimental factors being manipulated. In the table, a yes means that there was statistically significant difference for one of the main effects or interaction, and a no means that there was not a statisically significant difference. As you can see, just by adding one more independent variable, the number of possible outcomes quickly become more complicated. When you conduct a 2x2 design, the task for analysis is to determine which of the 8 possibilites occured, and then explain the patterns for each of the effects that occurred.
One Factor at a Time and factorial experimental design for formulation of l-carnitine microcapsules to improve its ... - ScienceDirect.com
One Factor at a Time and factorial experimental design for formulation of l-carnitine microcapsules to improve its ....
Posted: Mon, 15 Jan 2024 08:00:00 GMT [source]
The following Yates algorithm table using the data for the null outcome was constructed. As seen in the table, the values of the main total factorial effect are 0 for A, B, and AB. This proves that neither dosage or age have any effect on percentage of seizures.
More specifically, in both cases, wearing a hat adds exactly 6 inches to the height, no more no less. Blinding is especially important in studies where subjective response are considered as outcomes. This is because certain responses can be modified based on the knowledge of the experiment group that they are in.
When multiple dependent variables are different measures of the same construct - especially if they are measured on the same scale - researchers have the option of combining them into a single measure of that construct. Recall that Schnall and her colleagues were interested in the harshness of people’s moral judgments. To measure this construct, they presented their participants with seven different scenarios describing morally questionable behaviors and asked them to rate the moral acceptability of each one. Although the researchers could have treated each of the seven ratings as a separate dependent variable, these researchers combined them into a single dependent variable by computing their mean. When an experiment includes multiple dependent variables, there is again a possibility of carryover effects.


No comments:
Post a Comment